Electric power is very important in our daily life. It lights our homes, runs machines, powers industries, and keeps modern life running. Without a steady power supply, life would be very difficult. Traditionally, most electricity comes from coal, gas, and other fossil fuels. But these energy sources pollute the air, harm the environment, and contribute to climate change.
Renewable energy is clean, safe, and sustainable. It provides electric power without harming the planet. Renewable energy sources are now essential for a better future. They also help in energy security, create jobs, and reduce the impact of global warming.
In this article, we will discuss the top renewable energy sources for electric power. You will learn how they work, their benefits and challenges, and how they contribute to clean, reliable electricity. We will also cover tips for using renewable energy efficiently and five common FAQs.
1. Solar Power

Solar power is one of the most widely used renewable energy sources for electric power. It captures energy from sunlight and converts it into electricity.
How Solar Power Works
- Solar panels contain small units called photovoltaic (PV) cells.
- PV cells convert sunlight into electricity.
- The electricity can be used immediately, stored in batteries, or sent to the main power grid.
Solar power is widely used for homes, offices, and industries. It is especially helpful in sunny regions. Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, solar farms, and even floating on water.
Pros of Solar Power
- Clean and eco-friendly.
- Reduces electricity bills for homes and businesses.
- Low maintenance costs after installation.
- Can be used in remote areas without grid access.
Cons of Solar Power
- Efficiency drops on cloudy or rainy days.
- High initial installation cost.
- Requires space for large-scale power generation.
Solar power is a flexible solution. It contributes to power generation at both small and large scales. Advances in technology are making solar panels more efficient and affordable every year.
2. Wind Power
Wind power is another important source of renewable electric power. It uses the wind to turn turbines, which generate electricity.
How Wind Power Works
- Wind moves the blades of a wind turbine.
- The spinning turbine drives a generator that produces electricity.
- Electricity can be used locally or fed into the main power supply network.
Wind power is ideal for areas with strong and consistent winds, such as plains, hills, and offshore regions. Large wind farms are built to supply electricity to the grid.
Pros of Wind Power
- Clean and renewable energy.
- Can generate a significant amount of electricity for communities and industries.
- Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Works well with other renewable sources like solar.
Cons of Wind Power
- Output depends on wind speed and weather conditions.
- Wind turbines can affect birds and wildlife.
- Some people find turbines noisy or visually disruptive.
Modern turbine designs are improving efficiency and reducing costs. Wind power contributes to sustainable power generation and is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Hydropower
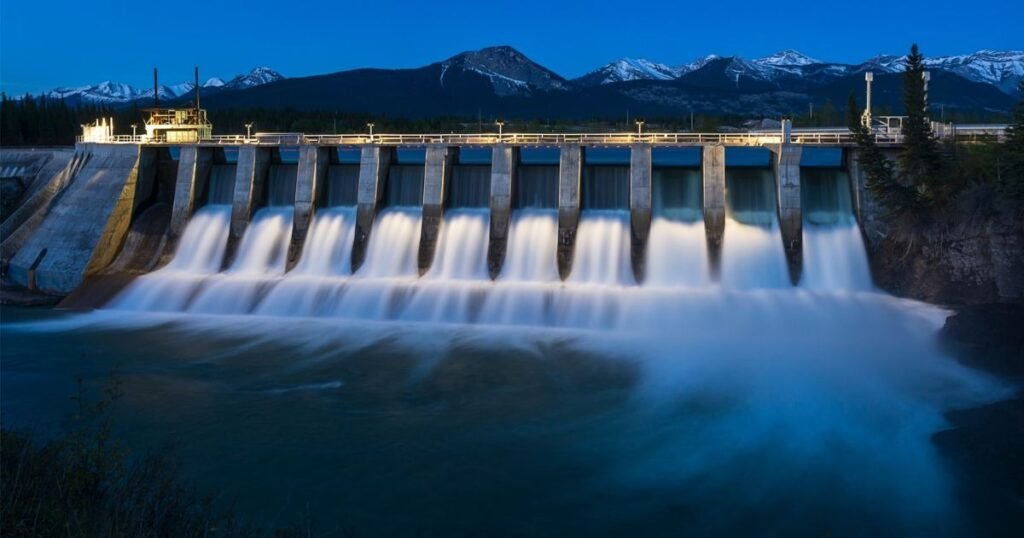

Hydropower is one of the oldest and most reliable sources of renewable electric power. It uses flowing water to spin turbines and generate electricity.
How Hydropower Works
- Water flows from rivers or dams through turbines.
- Turbines spin a generator to produce electricity.
- Extra electricity can be stored in pumped storage systems for later use.
Hydropower is used worldwide. It is a key source of base-load power because it provides consistent electricity even when solar or wind power is low.
Pros of Hydropower
- Highly reliable and stable.
- Can generate large amounts of electricity.
- Storage options allow balancing supply and demand.
- Supports power distribution by feeding electricity into the grid efficiently.
Cons of Hydropower
- Dams can disrupt ecosystems and displace communities.
- High initial construction costs.
- Electricity output can fall during droughts or low water periods.
Hydropower is a cornerstone of clean electric power. It ensures a continuous supply for urban centers, industries, and rural areas.
4. Biomass Energy
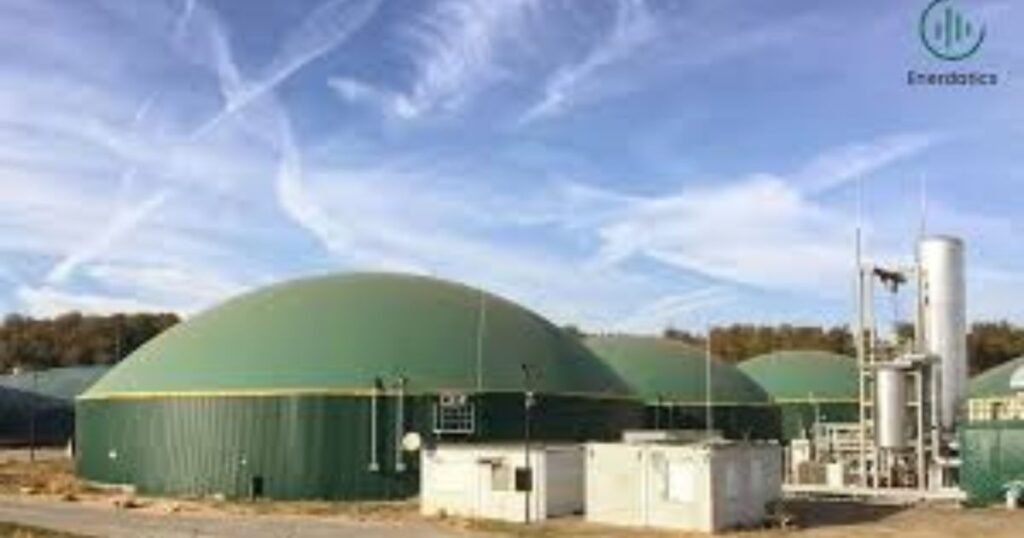

Biomass energy is electricity made from organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, or animal residues.
How Biomass Energy Works
- Biomass is burned or converted into gas to produce heat.
- Heat generates steam that spins turbines.
- Turbines create electricity that goes to homes or the main power supply network.
Biomass energy is widely used in rural areas where agricultural waste is abundant. It complements solar and wind energy by providing constant electricity.
Pros of Biomass Energy
- Uses waste materials, reducing landfill and pollution.
- Can provide electricity continuously, unlike intermittent sources.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
Cons of Biomass Energy
- Can produce emissions if not managed correctly.
- Requires land and resources for fuel production.
- Transporting biomass to power plants may be costly.
Biomass is an important part of renewable power generation, especially in agricultural and rural areas.
5. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy comes from the heat stored under the Earth’s surface. It is a reliable and steady source of electric power.
How Geothermal Energy Works
- Hot water or steam is brought from underground reservoirs.
- The steam drives turbines connected to generators.
- Electricity is fed into the local or national power supply network.
Geothermal energy is especially useful in areas with volcanic or tectonic activity.
Pros of Geothermal Energy
- Provides continuous electricity.
- Very low greenhouse gas emissions.
- Small land area needed for power plants.
Cons of Geothermal Energy
- Only feasible in certain geological regions.
- High initial cost for drilling and plant construction.
- Potential for minor seismic activity.
Geothermal energy supports reliable power distribution, providing electricity all day and night.
6. Ocean Energy
Ocean energy uses tides, waves, and currents to generate electric power. It is an emerging but promising renewable source.
How Ocean Energy Works
- Tidal turbines spin when water moves during high and low tides.
- Wave energy converters harness the motion of ocean waves.
- Electricity is sent to the power supply network.
Ocean energy has great potential for coastal areas.
Pros of Ocean Energy
- Predictable energy source.
- Minimal land use.
- Can complement other renewable sources.
Cons of Ocean Energy
- Expensive technology and maintenance.
- Potential harm to marine life.
- Challenging to maintain in harsh ocean environments.
Ocean energy is slowly becoming a reliable part of global electric power production.
Benefits of Renewable Energy

- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Security: Reduces reliance on imported fuels.
- Job Creation: Provides employment in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Reliable Power Distribution: Local renewable systems reduce transmission losses and improve energy access.
- Sustainable Power Supply: Renewable sources ensure long-term electricity availability.
Challenges of Renewable Energy
- Weather-Dependent: Solar and wind power vary with weather.
- High Startup Costs: Some systems need significant investment.
- Grid Compatibility: Power grids may need upgrades to handle renewable electricity.
- Storage Needs: Batteries or pumped storage systems are required for constant supply.
Despite these challenges, renewable energy is becoming more efficient and cost-effective every year.
Tips for Using Renewable Energy
- Combine solar, wind, and hydropower to ensure constant electricity.
- Use batteries or pumped storage to save extra electricity.
- Implement smart grids for better power distribution.
- Encourage residential use of solar panels or small wind turbines.
- Monitor energy usage to reduce waste and increase efficiency.
Conclusion
Renewable energy is the future of electric power. Solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, and ocean energy all play a vital role in providing clean and safe electricity. These energy sources reduce pollution, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and help protect the environment.
They also support a reliable and steady power supply for homes, businesses, and industries. By investing in renewable energy, we can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and create a sustainable energy system for future generations. Electric power from renewable sources is no longer just an idea; it is essential for a greener and healthier world.
FAQs
1. Which renewable energy is most reliable?
Hydropower and geothermal are very reliable and provide electricity all day and night.
2. Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels completely?
Yes, with a combination of sources and storage solutions, renewable energy can greatly reduce fossil fuel dependence.
3. How does renewable energy help power distribution?
Local renewable systems, like rooftop solar, reduce load on central grids and minimize transmission losses.
4. Is renewable energy expensive?
Installation can be costly, but operating costs are low. Prices are decreasing with new technology.
5. Are there risks with renewable energy?
Some systems, such as dams or turbines, can affect wildlife if not properly managed.