The proliferation of the industrial internet of things (IoT) is profoundly altering the modus operandi of factories. These things, which include machines, sensors, and systems, are now connected in real connection made. The outcome is the so-called “smart factories” that are more efficient, safer, and quicker. IIoT is utilized by enterprises to lower expenses, raise the level of quality, and remain in the market.
Factory output is under tremendous stress in the modern digital world. The corporate world needs to satisfy the global demand faster, and at the same time, meet the requirement of cutting down on waste. Traditional systems cannot keep up. This is where the IoT Technology Trends 2025 comes in. Linking machines with data it creates factories that think, adapt, and improve.
1. Improved Operational Efficiency with Internet of Things
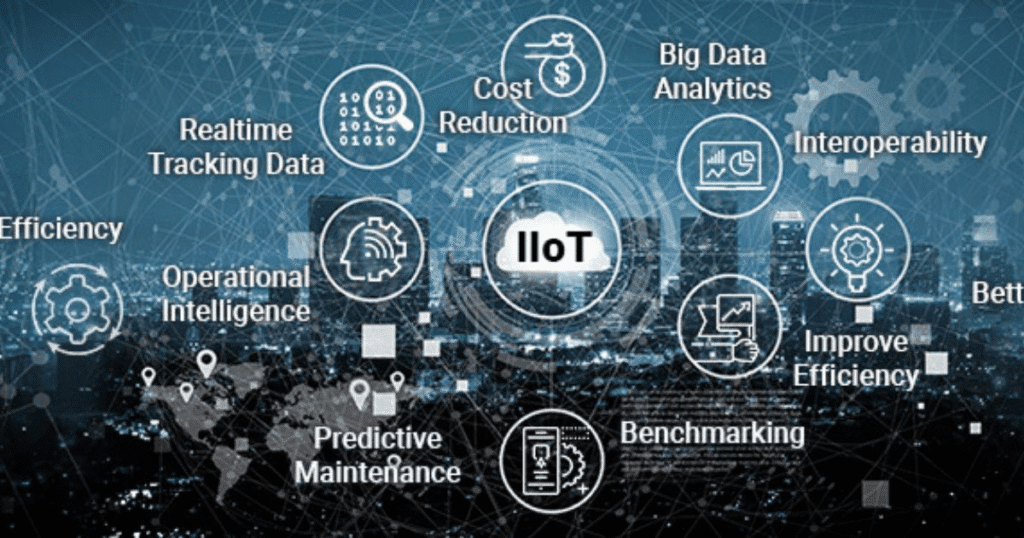
Smart factories thrive on efficiency. The internet of things allows machines to talk to each other. Real-time data from sensors gives workers insight into every process. This removes guesswork and speeds up decision-making.
Key Features:
- Machines share data instantly.
- Energy use is tracked and optimized.
- Production bottlenecks are detected early.
Upsides
- Faster production cycles.
- Lower energy costs.
- Less waste in operations.
Low points
- Requires new system integration.
- Initial setup can be costly.
Advice:
Start with small pilot projects before scaling IIoT across all operations.
2. Predictive Maintenance Reduces Downtime

One of the biggest benefits of the Digital Network is predictive maintenance. Machines no longer break down without warning. Sensors monitor performance, temperature, and vibration. This data signals when maintenance is needed.
Standout Points
- Real-time machine health monitoring.
- AI-powered predictive alerts.
- Reduced emergency repairs.
Plus points
- Less unplanned downtime.
- Extended machine lifespan.
- Lower repair costs.
Hindrances
- Needs skilled staff to read data.
- Some older machines may not support sensors.
Suggestion:
Combine predictive maintenance with staff training to ensure maximum results.
3. Enhanced Quality Control in Smart Factories

Factories must meet strict quality standards. The Cyber Space of makes this possible with precision monitoring. Every stage of production is tracked. If an error occurs, the system alerts workers immediately.
Important Details
- Real-time product tracking.
- Automated defect detection.
- Consistent production quality.
Strong points
- Fewer defective products.
- Better customer satisfaction.
- Lower recall costs.
Detriments
- High reliance on accurate sensor data.
- Requires investment in advanced quality tools.
Recommendation:
Use IIoT to set quality benchmarks and monitor them continuously.
4. Better Supply Chain Visibility

The supply chain is the backbone of manufacturing. With the Digital Space , businesses can track raw materials and products in real time. This reduces delays and ensures smooth delivery.
Notable Features
- GPS tracking of shipments.
- Real-time inventory levels.
- Supplier performance monitoring.
Perks
- Reduced inventory shortages.
- Faster delivery times.
- Stronger supplier relationships.
Flaws
- Data privacy concerns in logistics.
- Needs advanced connectivity solutions.
Pro tip:
Integrate IIoT with ERP systems for full supply chain visibility.
5. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability

Factories use large amounts of energy. The Online Platform helps reduce waste by tracking usage. Smart sensors show where energy is lost and suggest improvements.
Essential Features
- Energy use monitoring in real time.
- Automated power adjustments.
- Carbon footprint tracking.
Highlights
- Lower energy bills.
- Supports eco-friendly goals.
- Meets global sustainability standards.
Challenges
- High setup cost for sensors.
- Data overload without proper analysis.
Quick note:
Use IIoT dashboards to identify areas with the highest energy waste.
6. Worker Safety and Risk Management

Safety is vital in factories. The Future of Connected Technology creates safer workplaces by tracking worker conditions and equipment risks. Smart helmets and sensors can alert workers before accidents happen.
Main Attributes
- Wearable safety devices.
- Hazard detection sensors.
- Emergency alerts and shutdowns.
Strengths
- Fewer workplace accidents.
- Strong compliance with safety laws.
- Improved employee confidence.
Shortcomings
- Dependence on wearable devices.
- Workers may resist new technology.
Handy hint:
Introduce IIoT safety gear step by step to encourage adoption.
7. Faster Decision-Making with Data Insights
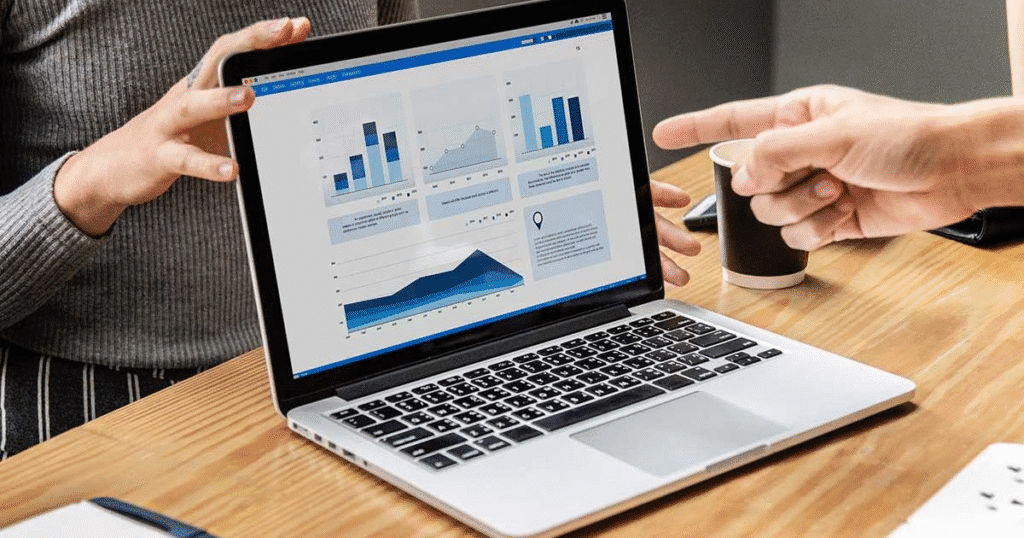
Factories need quick and accurate decisions. The Smart Devices and Connectivity delivers live data dashboards. Managers see problems as they happen and act fast.
Main Features
- Real-time dashboards.
- AI-driven insights.
- Cloud-based data sharing.
Positive aspects
- Faster response times.
- Data-driven strategies.
- Reduced human error.
Downsides
- Needs strong cybersecurity.
- Training is required to interpret data.
Useful reminder:
Use data visualization tools to make IIoT dashboards easy for all staff.
8. Scalability and Flexibility
Smart factories must adapt to demand changes. The Connected Devices makes scaling easier. Systems can grow without major disruptions.
Core Highlights
- Modular system design.
- Cloud integration.
- Remote machine management.
Strengths
- Easy to expand production.
- Adapts to changing markets.
- Reduces downtime during scaling.
Drawbacks
- High reliance on cloud systems.
- Needs reliable Smart Web connectivity.
Key takeaway:
Plan IIoT architecture with future growth in mind.
9. Cost Reduction Through Automation

Automation is key in modern factories. The Digital Eco system powers automation by connecting machines. This lowers labor costs and increases speed.
Top Specifications
- Automated machine controls.
- Robotic process integration.
- Smart scheduling systems.
Benefits
- Reduced labor costs.
- Higher production rates.
- Consistent output.
Limitations
- May reduce some job roles.
- Needs high upfront investment.
Editor’s note:
Balance automation with skilled human oversight for best results.
10. Competitive Advantage in Global Markets

In today’s world, competition is global. The Smart Connectivity Systems gives smart factories an edge. Companies can offer better quality, faster delivery, and lower costs.
Product Highlights
- Real-time customer data.
- Advanced production systems.
- Stronger global reach.
Advantages
- Improved brand reputation.
- Higher market share.
- Long-term business growth.
Disadvantages
- Competitors may adopt similar systems.
- Constant upgrades are needed.
Tip:
Use IIoT to create unique customer value, not just faster production.
Conclusion
The internet of things is not just a trend. It is the future of smart factories. IIoT provides a wide range of benefits, such as predictive maintenance and energy efficiency. Facilities that implement IIoT technology can go through the same processes with less time, increased safety and reduced costs, as well as lower their operating expenses.
The industrial IoT Technology Trends changes the industries that connect the machines, employees, and organization. It is thus, possible for corporations to satisfy global demand without compromising on their sustainability efforts. Any smart factory that would make an IIoT investment now was the future market leader of tomorrow.
If you desire the manufacturing plant to be effective, safe, and have a competitive advantage over the others, then the time to use the industrial Smart Homes and Automation Tech is now.
FAQs
What role does IoT play in smart manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing IoT establishes connections between devices, sensors, and software. Through this, you can have instant operations and data insights that improve the output quality and reduce the downtime.
How does IIoT help with predictive maintenance?
IIoT just like a doctor who uses sensors to monitor the health of machines. The information indicates the beginning of the malfunction so that the maintenance can be done earlier than the breakdown. In this manner, costs and downtime are reduced.
Is the internet of things secure?
Yes, but only if accompanied by strong cybersecurity. Smart factories must incorporate encryption, firewalls, and secure cloud systems as measures of defense against threats to data.
What industries benefit the most from the industrial internet of thing?
Top beneficiaries of industrial Next-Gen Connectivity are the auto, electronic, pharmaceutical, and heavy manufacturing sectors. Such industries are closely tied to the accurate manufacturing, the vast-scale conduct of operations, and the maintenance of high-quality standards and all these aspects are largely improved by the IIoT.
What distinguishes the Industrial Digital Era of Thing?
smart homes; the (IoT) is eventually the same as wearables, and other daily applications.. The industrial (IoT) or the industrial is a factory and industries’ domain. Its primary focus is on efficiency, safety, and large-scale production systems.